Frequently Asked Questions
Obesity is determined by having a body mass index (BMI) of 25 or higher. It means having excess body fat, which can lead to various health issues.
Weight loss begins right after the surgery. Typically, patients who have undergone bariatric surgery can resume work after one week.
The main reasons for obesity are unhealthy eating habits, lack of physical activity, genetic factors, hormonal imbalances and certain medications.
No, when it comes to weight loss, there are no shortcuts or quick fixes. It's a lifelong commitment that requires consistent effort and a balanced approach.
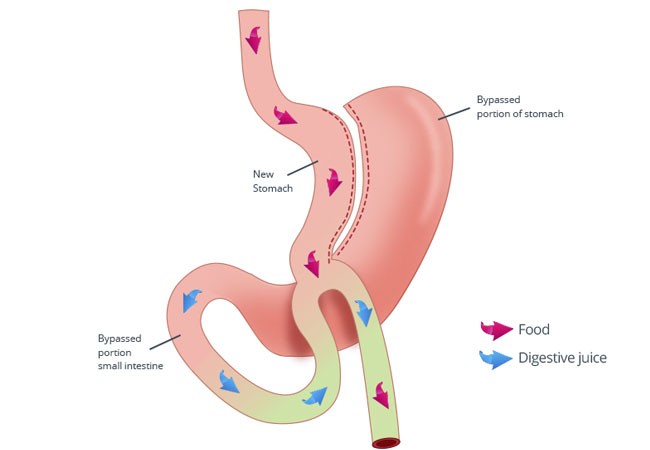
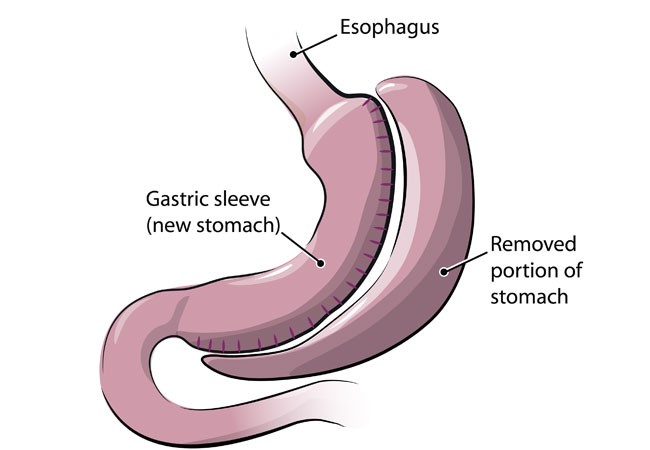
After bariatric surgery, individuals can lose between 40 and 60 kg or even up to 70 kg, depending on their initial weight. Weight loss begins immediately after the surgery.
The selection of exercise plays a role in weight reduction. Both aerobic and anaerobic exercises are beneficial. Consistency and frequency of exercise are important for weight loss. Some individuals may struggle with maintaining their exercise routine, so it's important to balance calorie intake and expenditure.
Delivering world class medical care in the field of
Diabetes, Thyroid, Endocrinology and Obesity
with
precision and compassion.
X

 Home
Home  Booking
Booking
 Chat Now
Chat Now  Call Us
Call Us